Cosmology
@Cosmology0
Follow us for more
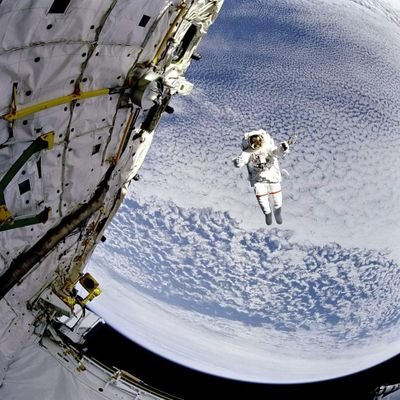
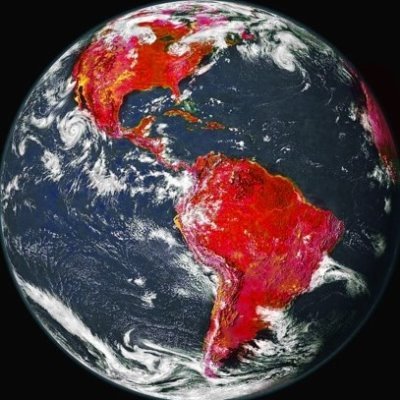
A re-entry to Earth, captured by NASA's astronaut
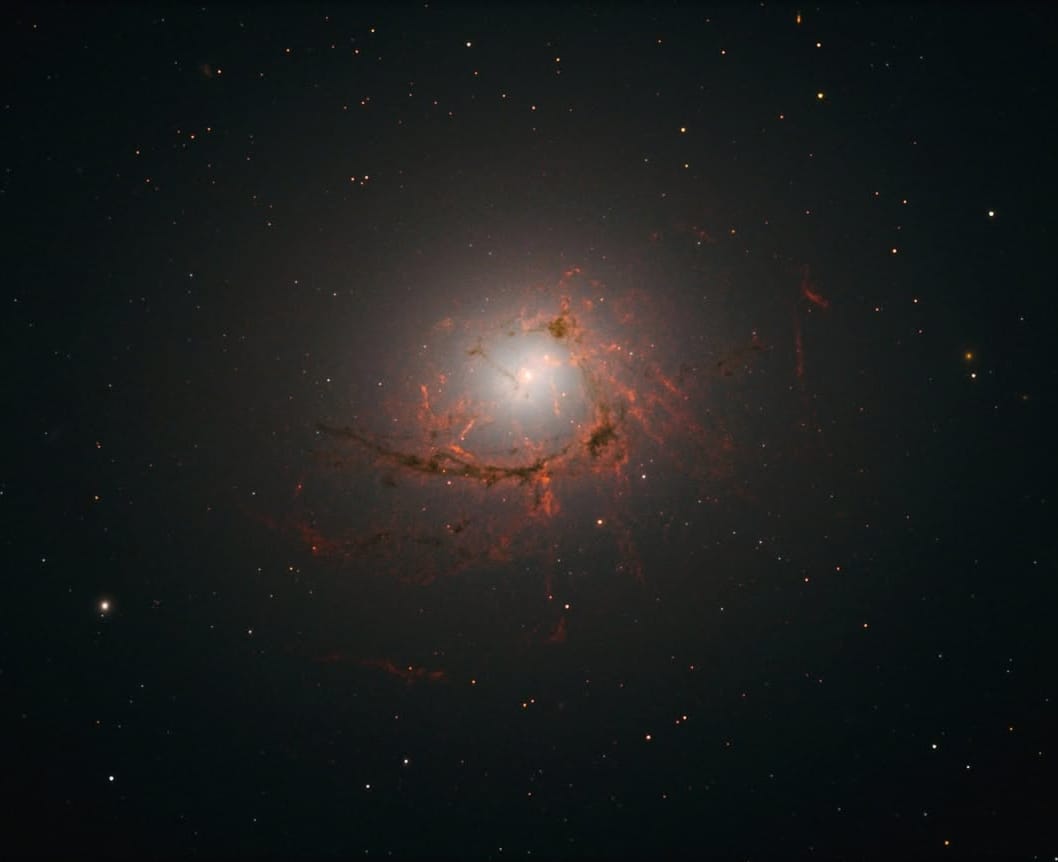
NGC 4696, a galaxy about 150 million light-years away, known for its dark red filaments of gas and dust that appear connected to its core, where a supermassive black hole likely resides and will eventually consume these filaments. It's the largest galaxy in the Centaurus cluster.

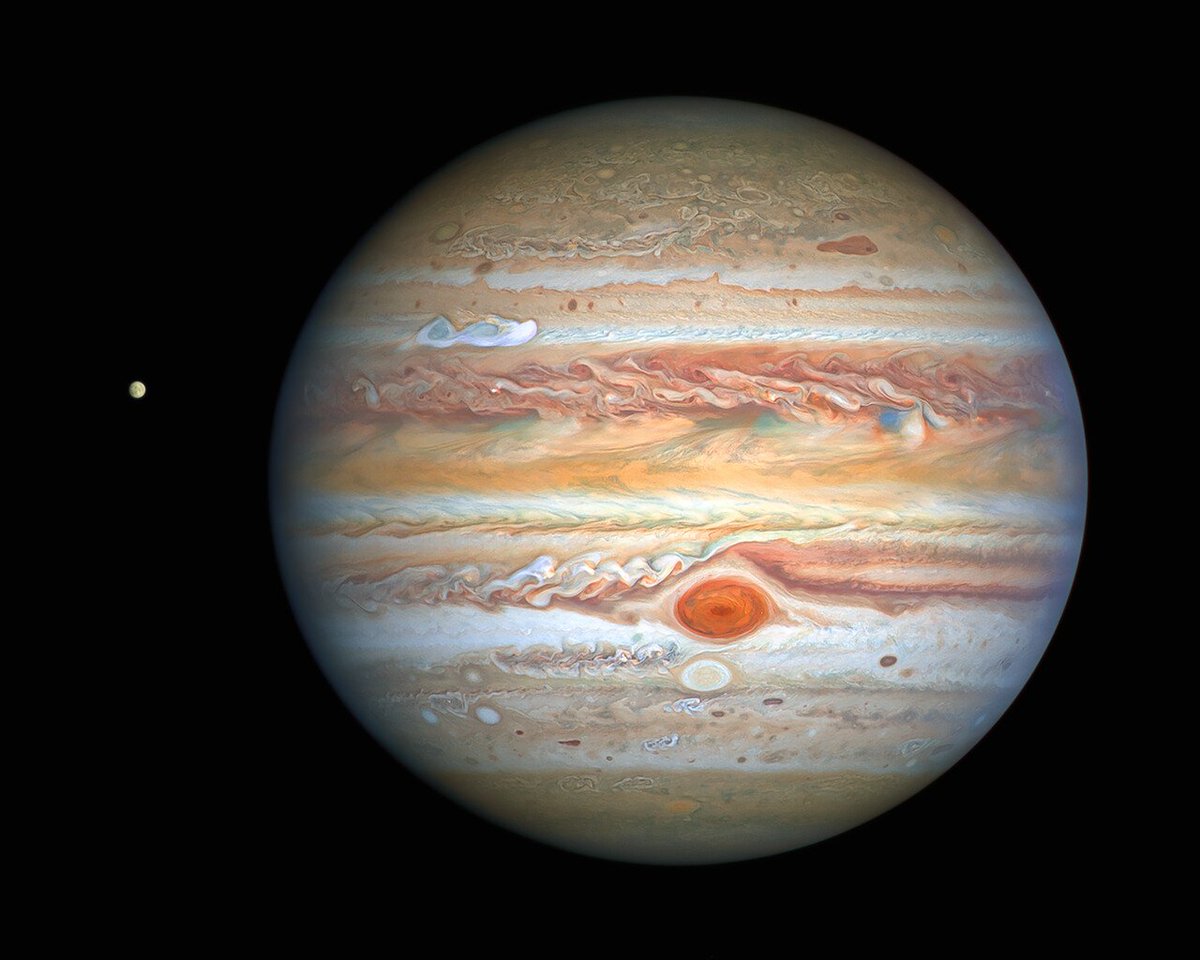
Jupiter. Captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope on August 25, 2020, when 653 million km from Earth. The image shows turbulent atmosphere with a new storm and changes in the Great Red Spot, plus its icy moon Europa.
NGC 1317, a vast, face-on spiral galaxy over 50 million light-years away, featuring an inner ring of hot, young stars studied by Hubble to understand star formation. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Lee and the PHANGS-HST Team.

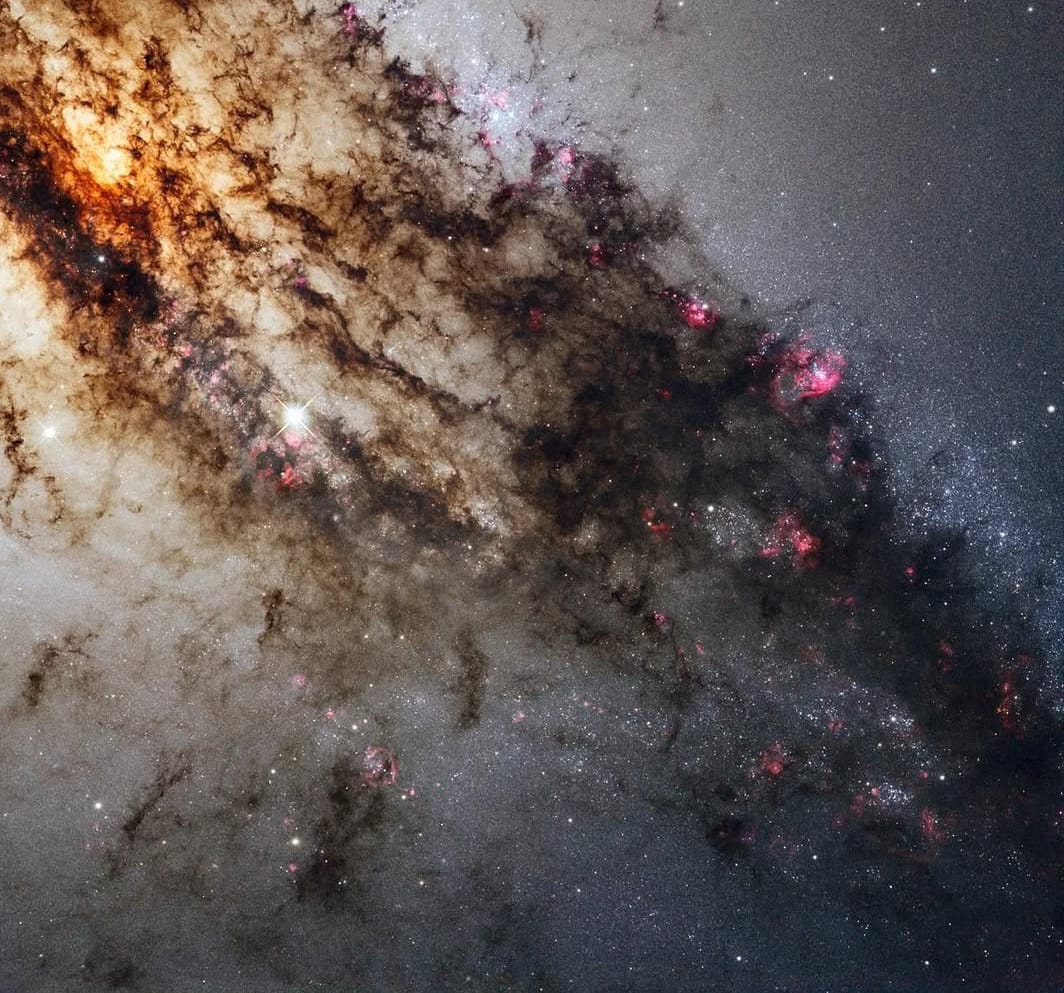
Centaurus A, features a bright orange region in its upper left, with dark dust flowing diagonally downwards. The background is a hazy space filled with distant stars, and pink areas of new star formation are visible within the dust.

If you could swap Earth for any fictional planet from sci-fi, where would you want to live and what unique features make it your ideal cosmic home? 🚀🪐 #SciFiDreams
Imagine space as a giant storybook, where stars sparkle like memories, lighting up the cosmic night with tales written across the endless pages of the universe. #StellarStories #GalacticTales #SpaceWonders #AstroAdventures
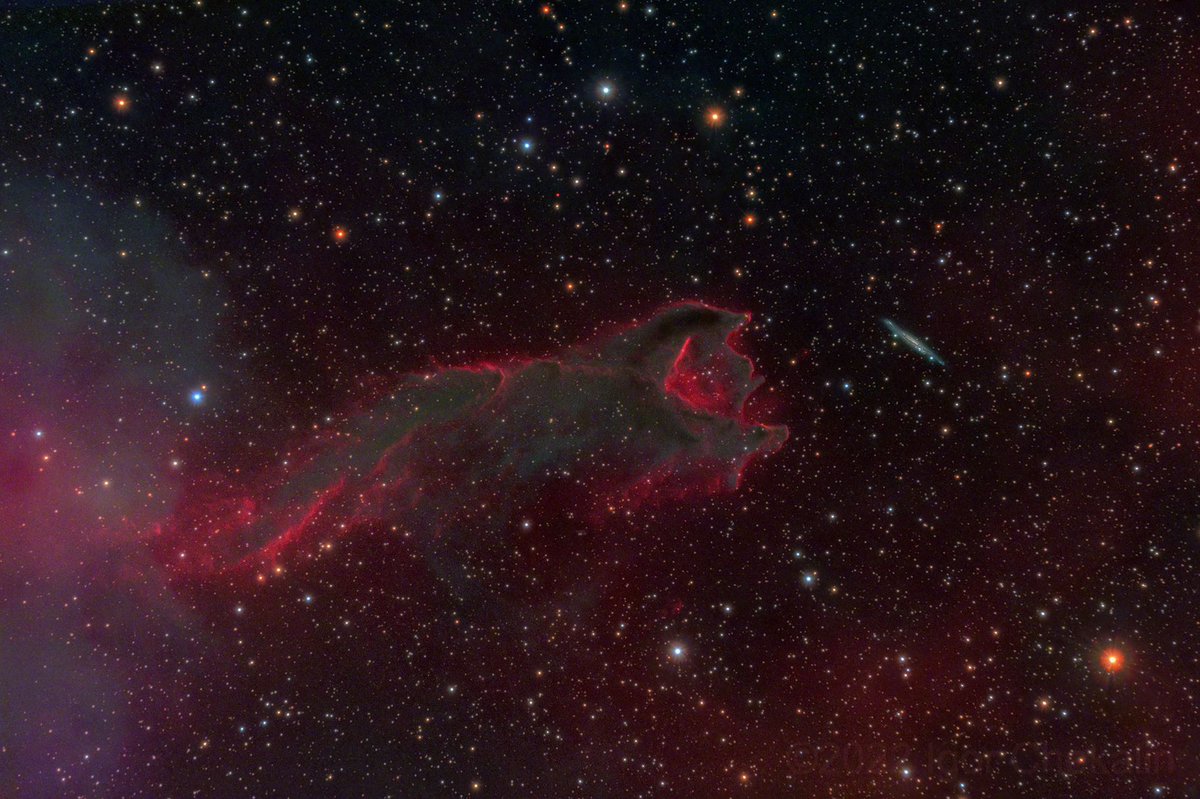
CG4, also known as the Cometary Globule 4, is a dark nebula located in the constellation Puppis. It is a unique cosmic structure resembling a comet with a bright head and a faint tail. CG4 is about 1,300 light-years away from Earth and is notable for its distinct shape.

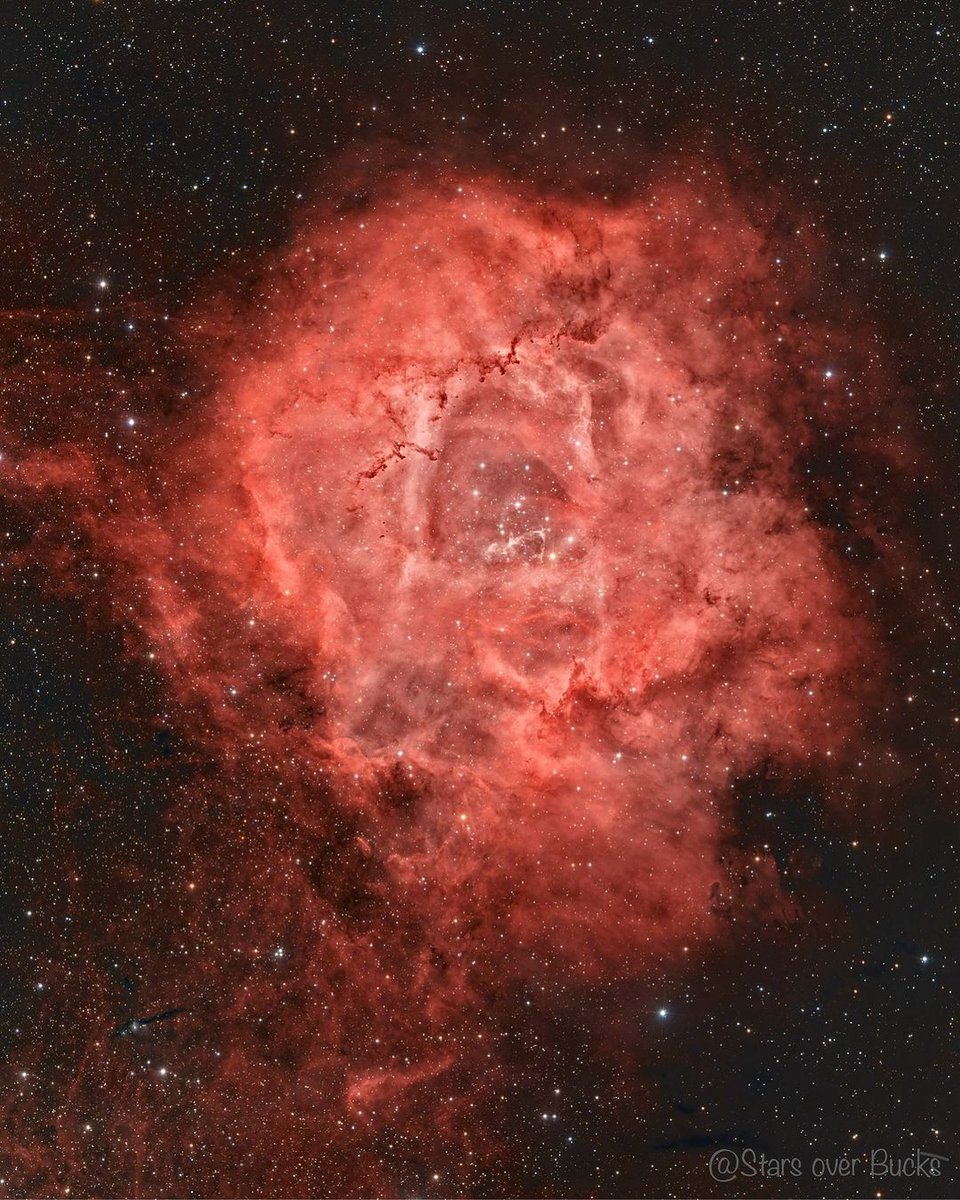
The Rosette Nebula and star cluster (NGC 2244) in the constellation of Monoceros. This is a star forming region that is 5000 light years away and measures 130 light years across.

Wormholes, theoretical shortcuts in spacetime, may enable faster-than-light travel. Stability requires exotic matter, and their existence is yet unconfirmed, remaining a captivating but speculative concept. #wormholes #SpaceExploration
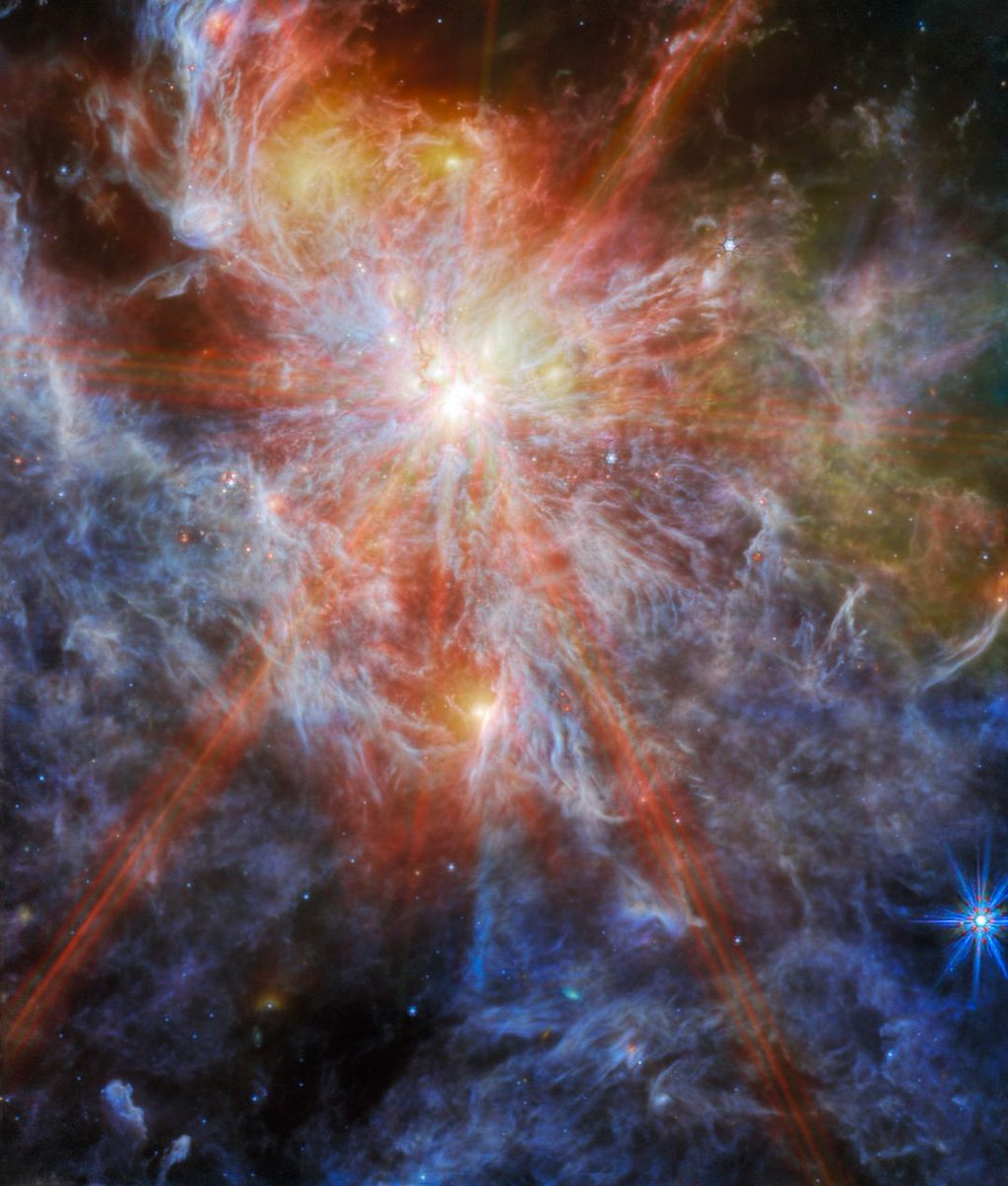
N79, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, is a region where stars are actively forming. Through mid-infrared observations, the Webb telescope unveils the luminous presence of gas, dust, and emerging young stars.

United States Tendances
- 1. #ใครในกระจกEP5 9,333 posts
- 2. #happybdayTYGA N/A
- 3. $NVDA 51.5K posts
- 4. GeForce Season 4,257 posts
- 5. Peggy 36K posts
- 6. $LMT $450.50 Lockheed F-35 N/A
- 7. Martha 17.9K posts
- 8. Sonic 06 3,416 posts
- 9. Saba 10.7K posts
- 10. Jason Crow 1,472 posts
- 11. Comey 51.3K posts
- 12. Stargate 5,484 posts
- 13. Poverty 49.8K posts
- 14. MLB TV 1,963 posts
- 15. Sumrall 1,528 posts
- 16. Halligan 22.8K posts
- 17. Nvidia 61.6K posts
- 18. NASA 48.1K posts
- 19. #ComunaONada 5,200 posts
- 20. Dearborn 411K posts
Something went wrong.
Something went wrong.