#javainspires hasil pencarian
Q15. What are short-circuiting operations? These are operations that may terminate early without processing all elements, like findFirst(), anyMatch(), allMatch(), and noneMatch(). #JavaInspires
Q4. What is lazy evaluation in Streams? Streams are lazily evaluated, meaning intermediate operations are not executed until a terminal operation is invoked. This enables efficient computation. #JavaInspires
Q12. How does the reduce() operation work? It performs a reduction on stream elements using an associative accumulation function and returns an Optional or a specified identity value. #JavaInspires
Q5. How do you create a Stream in Java? Common ways include: - Using collection.stream() or collection.parallelStream() - Using Stream.of() for fixed elements - Using Arrays.stream(array) - Using Stream builders or generators. #JavaInspires
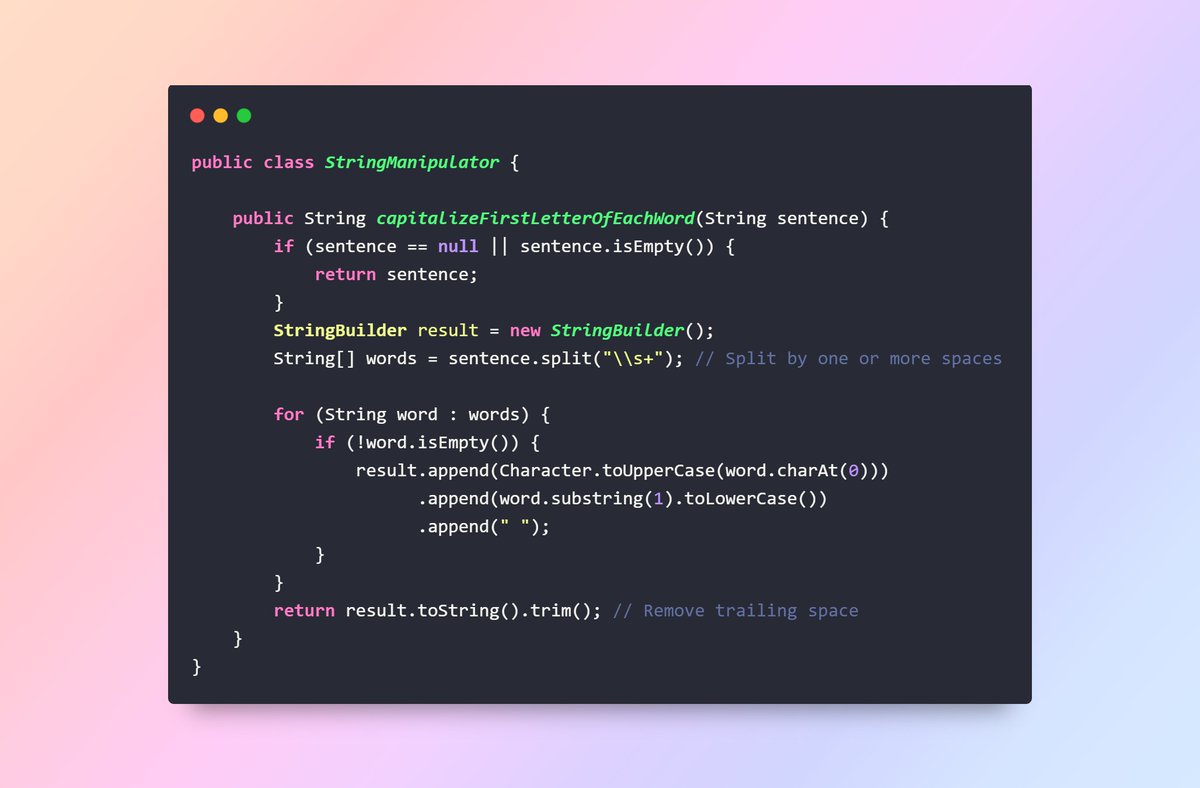
Q6. What is the difference between map() and flatMap()? - map() transforms each element individually and returns a Stream of elements. - flatMap() flattens nested Streams into a single Stream, useful for handling collections within collections. #JavaInspires
Q3. What are intermediate and terminal operations in Streams? Intermediate operations: Return another Stream (e.g., map, filter, distinct, sorted). Terminal operations: Produce a result or side-effect (e.g., collect, forEach, reduce). #JavaInspires
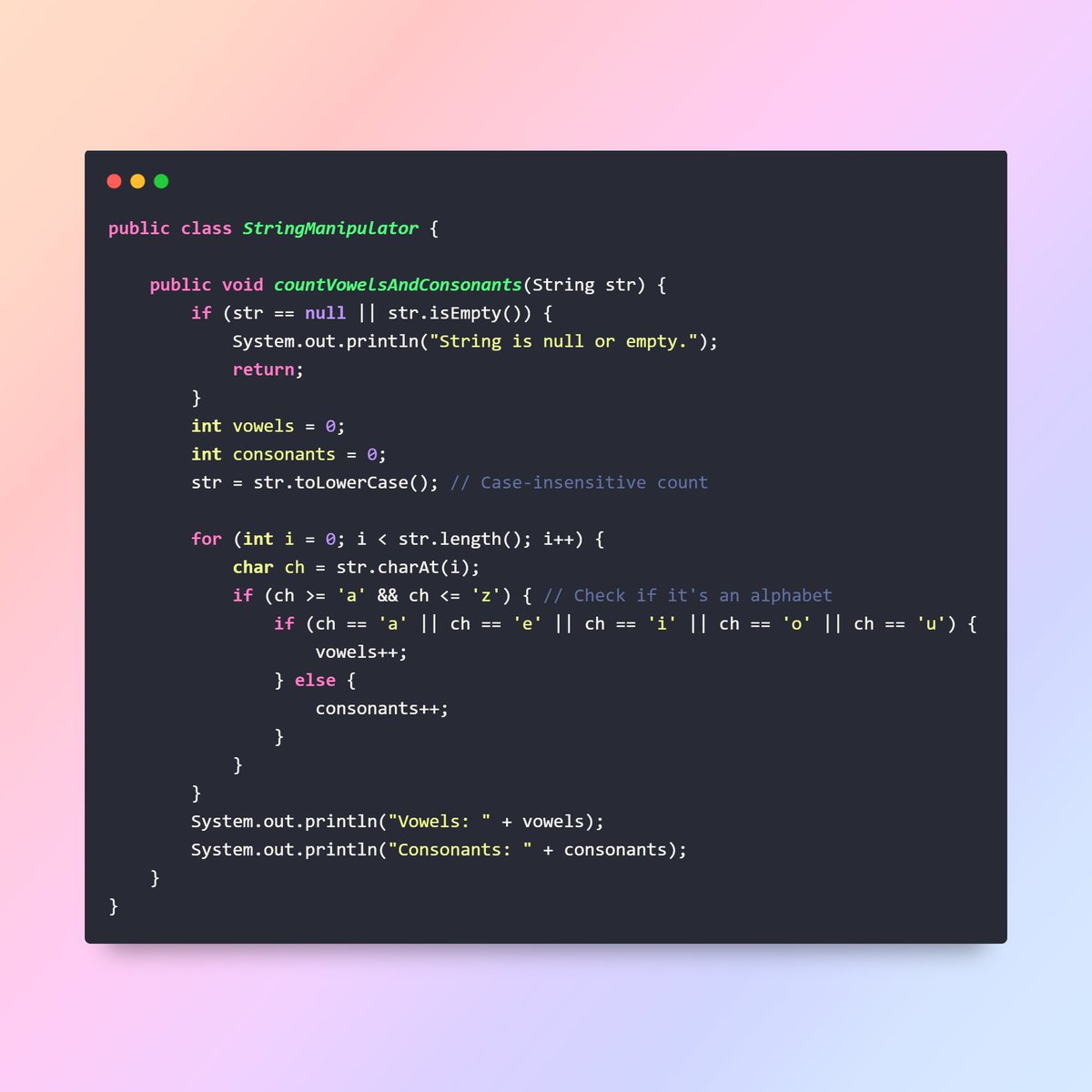
Q1. What is a Stream in Java? A Stream is a sequence of elements supporting functional-style operations. It allows processing data declaratively using operations like map, filter, and reduce without modifying the underlying data source. #JavaInspires
Q11. What happens if a Stream is reused after a terminal operation? A Stream cannot be reused. Once a terminal operation is executed, the Stream is considered consumed and closed. #JavaInspires
Q15. What are short-circuiting operations? These are operations that may terminate early without processing all elements, like findFirst(), anyMatch(), allMatch(), and noneMatch(). #JavaInspires
Q14. Can a Stream handle null values? No, passing null to Stream operations (like Stream.of(null)) will throw a NullPointerException. #JavaInspires
Q13. What is the difference between findFirst() and findAny()? - findFirst() returns the first element in encounter order. - findAny() may return any element, optimized for parallel execution. #JavaInspires
Q12. How does the reduce() operation work? It performs a reduction on stream elements using an associative accumulation function and returns an Optional or a specified identity value. #JavaInspires
Q11. What happens if a Stream is reused after a terminal operation? A Stream cannot be reused. Once a terminal operation is executed, the Stream is considered consumed and closed. #JavaInspires
Q10. What are some common terminal operations? collect(), forEach(), count(), reduce(), min(), max(), and findFirst(). #JavaInspires
Q9. What is the advantage of using parallel streams? Parallel streams divide the stream elements into multiple substreams processed concurrently, leveraging multi-core processors for better performance on large datasets. #JavaInspires
Q8. What does the filter() method do? It filters elements based on a given predicate, returning a Stream containing only the elements that match the condition. #JavaInspires
Q7. How can you convert a Stream to a List or Set? Use collectors:#JavaInspires List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList()); Set<Integer> set = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Q6. What is the difference between map() and flatMap()? - map() transforms each element individually and returns a Stream of elements. - flatMap() flattens nested Streams into a single Stream, useful for handling collections within collections. #JavaInspires
Q5. How do you create a Stream in Java? Common ways include: - Using collection.stream() or collection.parallelStream() - Using Stream.of() for fixed elements - Using Arrays.stream(array) - Using Stream builders or generators. #JavaInspires
Q4. What is lazy evaluation in Streams? Streams are lazily evaluated, meaning intermediate operations are not executed until a terminal operation is invoked. This enables efficient computation. #JavaInspires
Q3. What are intermediate and terminal operations in Streams? Intermediate operations: Return another Stream (e.g., map, filter, distinct, sorted). Terminal operations: Produce a result or side-effect (e.g., collect, forEach, reduce). #JavaInspires
Q2. How is a Stream different from a Collection? Collections store data, while Streams process data. Streams do not store elements; they provide a pipeline to handle data from a source like a collection, array, or I/O channel. #JavaInspires
Q1. What is a Stream in Java? A Stream is a sequence of elements supporting functional-style operations. It allows processing data declaratively using operations like map, filter, and reduce without modifying the underlying data source. #JavaInspires
Designing a Distributed Caching Strategy #JavaInspires #Tech javainspires.blogspot.com/2025/08/design…
Graceful Shutdown in Spring #JavaInspires #SpringBoot #Spring 224springboot.blogspot.com/2025/09/gracef…
Debugging Spring Boot Applications in IntelliJ IDEA #JavaInspires #IntelliJIDEA #Jetbrains #Tech #Programming javainspires.blogspot.com/2025/08/debugg…
Filters and Listeners in Java EE #Java #Tech #JavaInspires javainspires.blogspot.com/2025/08/filter…
How to use the Collectors.groupingBy method from the Java Streams API to group a list of objects. #Java #JavaInspires

What is @Qualifier annotation in Spring? #JavaInspires #interviewquestions #Java javainspires.blogspot.com

Something went wrong.
Something went wrong.
United States Trends
- 1. Bengals 71.1K posts
- 2. Denny 11.3K posts
- 3. Chiefs 54.1K posts
- 4. Larson 10.1K posts
- 5. Bills 123K posts
- 6. Mahomes 17.6K posts
- 7. Bears 80.8K posts
- 8. #NASCAR 10.4K posts
- 9. Packers 65.9K posts
- 10. Panthers 54.4K posts
- 11. Josh Allen 9,910 posts
- 12. Cam Little 13.5K posts
- 13. Brock Bowers 3,112 posts
- 14. Cole Bishop 1,902 posts
- 15. Raiders 32K posts
- 16. Jags 4,683 posts
- 17. Joe Flacco 7,251 posts
- 18. McDermott 1,731 posts
- 19. Byron 11.1K posts
- 20. Colts 41.6K posts